What is ISRO’s Sun mission ? Aditya L1 | ISRO India
(Launch: September 2, 2023 at 11:50 am )

Aditya L1 is India’s space mission designed to study the Sun. The special thing about this spacecraft is that it will orbit around a point called Lagrange point 1 (L1), which is about 1.5 million kilometers away from Earth in the direction of the Sun. Aditya L1
Why is this important? Well, being at L1 allows the spacecraft to always have a clear view of the Sun, without any interruptions like when the Sun gets blocked by Earth. This is super useful for observing what’s happening on the Sun and how it affects space weather in real time.
Aditya L1 carries seven tools (we call them “payloads”) that help us look at different parts of the Sun. Imagine the Sun like a big onion – we want to study its outer layers, its middle part, and even the inside. Some of these tools look at the light coming from the Sun, others check the particles and magnetic fields around it.
From its special spot at L1, four tools directly watch the Sun’s surface, while the other three tools study the things around L1, like particles and fields. This helps us learn a lot about how the Sun’s behavior affects the space between planets. Sun mission
The data collected by Aditya L1’s tools will help us solve some big questions. For instance, we want to understand why the Sun’s outer layer is much hotter than its surface, how big explosions (called coronal mass ejections) happen on the Sun, and what causes events like solar flares. We also want to figure out more about space weather and how particles and fields move around in space. Aditya L1
In simpler words, Aditya L1 will be like a detective, looking at the Sun from a perfect spot to help us learn about its secrets and how it influences the space around us.
Aditya-L1 has important goals in the field of science

let’s dive deeper into each of these goals in simpler terms:
- Understanding the Upper Sun Layers: Aditya-L1 wants to know more about the Sun’s outer layers, which are like its skin. These layers are called the chromosphere and corona. Imagine it as studying the outside of a hot cup of tea to learn about the steam above it.
- Solving Solar Mysteries: Scientists are like space detectives. They want to solve puzzles about the Sun. One mystery is why the outer layers become so hot and how they create huge explosions (like fireworks in space) called coronal mass ejections. Aditya-L1 is like a detective’s magnifying glass, helping us look closely. ISRO India Sun mission
- Studying Particles from the Sun: Imagine tiny, super-hot particles and super-charged stuff coming from the Sun. Aditya-L1 collects information about these tiny things. It’s like studying ants in an anthill to understand how they move and why. Aditya L1
- Cracking the Corona Puzzle: Think of the Sun’s corona like a fiery halo around it. But here’s the puzzle: it’s way hotter than the Sun’s surface! Aditya-L1 is like a puzzle solver, trying to figure out why the corona is so hot and what makes it that way. Sun mission
- Checking Coronas and Loops: Imagine checking the temperature of water in a pool or counting the number of fish in a pond. Aditya-L1 does similar things, but for the Sun’s corona and the loops that stick out from it. These loops are like the Sun’s hair blowing in the space wind.
- Unveiling Solar Eruptions: Have you seen fireworks burst in the sky? The Sun has its own kind of fireworks called coronal mass ejections. Aditya-L1 helps us watch how these huge bursts grow, where they come from, and how they travel in space. ISRO India
- Spotting Solar Explosions: The Sun has different layers, like layers of a cake. Some layers play a big role in making solar events, like flares. Aditya-L1 helps us see the steps in these layers that create the fireworks on the Sun.
- Mapping Magnetic Fields: Imagine drawing a map that shows where the wind blows. Aditya-L1 draws a different kind of map—it shows how the Sun’s magnetic fields move in its outer layers. These fields are like invisible threads that shape the Sun’s behavior.
- Exploring Space Weather Drivers: Space is like an ocean, and the Sun’s stuff, called solar wind, is like waves in that ocean. Aditya-L1 helps us learn about this solar wind and how it affects the weather in space, just like real wind affects the sea. Aditya L1
So, Aditya-L1 is like a special telescope that watches the Sun closely. It helps scientists understand the Sun’s layers, its explosions, the tiny particles it sends out, and how it influences space weather around Earth. Just like detectives, scientists use Aditya-L1 to find answers to space mysteries. ISRO mission to Sun
Let’s break down the technologies and instruments used in the Aditya-L1 mission, listed in order of priority:
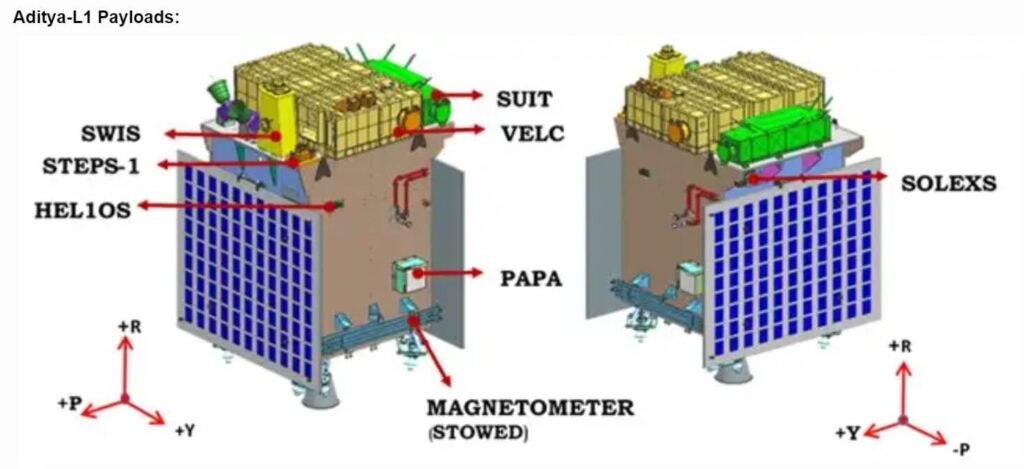
- Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC): This is the primary payload of Aditya-L1. VELC is designed to capture high-resolution images of the Sun’s corona, the outer atmosphere, at a closer distance than ever before. It’s equipped with 40 precise optical elements and will be kept at a controlled temperature of 22 degrees Celsius in space. Aditya L1 ISRO mission to Sun
- Ultraviolet Imager: Aditya-L1 carries an ultraviolet imager that helps capture specific wavelengths of light from the Sun. This tool allows scientists to study different aspects of the Sun’s behavior and characteristics. Sun mission
- X-ray Spectrometers (Two): These instruments are designed to detect X-rays emitted by the Sun. By analyzing these X-rays, scientists can learn more about the Sun’s temperature, composition, and other important properties. Aditya L1
- In-situ Instruments (Four): These instruments are responsible for measuring various parameters of the plasma (charged particles) around the Sun. They help us understand the characteristics of the space environment around the Sun.
- Automated Algorithm for CME Detection: A special algorithm has been created by scientists to automatically detect Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) using data from the VELC instrument. This is crucial for understanding these huge gas bubbles that the Sun releases and their impact on space weather. ISRO India
- Machine Learning Techniques: Advanced machine learning techniques have been implemented to enhance the detection of CMEs in the images captured by VELC. This involves using computer algorithms to recognize patterns and anomalies in the data.
- Support Cell for Data Analysis: A support cell has been established to assist guest observers in preparing science proposals and analyzing the data collected by Aditya-L1. This cell provides tools and training for users to understand and work with the observational data. ISRO India
- Clean Room Facilities: A specialized “Class 10” Clean Room has been constructed for assembling and testing the VELC payload. This controlled environment ensures that the delicate instruments are not contaminated by particles from Earth. ISRO mission to Sun
- Collaboration with Ground Observatories: Aditya-L1 collaborates with ground-based observatories like Kodaikanal Solar Observatory and Gauribidanur Radio Observatory to enhance its observations and deepen our understanding of the Sun-Earth relationship.

- Field Station Observations: Observations made from ground-based field stations complement the data gathered by Aditya-L1 and help provide a more comprehensive view of solar activity. ISRO mission to Sun
- Onboard Intelligence Algorithm: A unique onboard intelligence algorithm has been developed to automatically detect CMEs directly on Aditya-L1. This is a significant advancement compared to previous missions and adds a layer of autonomous decision-making to the spacecraft. Sun mission

The technologies and instruments used in the Aditya-L1 mission work together to gather valuable data about the Sun’s behavior, its outer layers, and the impacts on space weather. This mission involves a collaborative effort from various institutions and researchers to achieve its scientific objectives. ISRO mission to Sun
Read More
- What is Deepfake AI | Is Deepfake legal in India
- How AI can helpful at Ram Mandir Ayodhya Safety on January 22, 2024
- How Infosys loses $1.5 billion AI contract from global customer
- What is RAG Model ? How does rag work ? Future of Technology
- What is LLM large language model | Important LLM’s in 2023
- What happens if you go on the dark web | Is dark web illegal in India 2023?









0 Comments